PNIPU has discovered ways to enhance the durability of forest roads.
The study was published in the journal "Bulletin of PGTU. Forest. Ecology. Natural Resource Management." To reduce the costs of timber transportation, it is essential to lower the construction expenses of forest roads. However, it is crucial not to compromise the quality of these roads, particularly their resistance to deformation. This is vital for the socio-economic development of not only individual regions but also the economy of the country as a whole. According to data from Rosleskhoz, in 2023, revenues from the forestry sector to the federal budget of Russia amounted to 50.22 billion rubles, which is an eight percent increase compared to the previous period.
Utilizing geosynthetic membranes can lower the cost of timber and simultaneously enhance road efficiency. These membranes consist of interconnected sheets made from polymer material, resembling fabric in structure. They are placed between layers of construction material to prevent the subsidence of the road surface, allowing it to support more weight than a conventional surface.
Nonetheless, the deformation process of this material remains poorly studied. Researchers at Perm Polytechnic University investigated the stress-deformed state of geosynthetic membranes to understand how they settle under the weight of vehicle wheels.
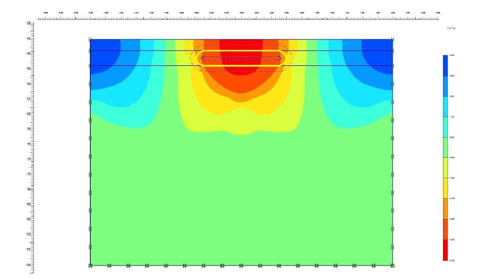
The polytechnic researchers examined the impact of the width and thickness of crushed stone membranes on subsidence. Using a computer model that replicated the load, they conducted two series of calculations with thicknesses of 0.2 and 0.4 meters at varying widths. For comparison, a similar modeling was also performed for a road without the corresponding covering.
“It turned out that the stress-deformed state of the geosynthetic material significantly depends on these parameters: for the covering to maintain its mechanical properties, the width must be 6-8 times greater than the thickness. If this ratio is 4 or less, the covering loses its stability under the weight of the wheels,” comments Vladimir Kleveko, Associate Professor of the Department of Roads and Bridges at PNIPU, Ph.D. in Technical Sciences.
The application of geosynthetic membranes in the construction of forest roads represents a promising direction for reducing timber transportation costs and enhancing the strength of the road surface. The research conducted by scientists at Perm Polytechnic University will improve the operational characteristics of forest roads, which is important for the socio-economic development of the region.